Labour unions have long shaped the economic and political landscape of advanced economies. Throughout the 20th century, they reduced inequality (Farber et al. 2021, Osorio-Buitron and Jaumotte 2015), improved working conditions (Rosenfeld 2019, Bryson et al. 2020), and influenced policies (Ahlquist 2017) and political systems (Acemoglu and Robinson 2013, Ogeda et al. 2024).
Despite fluctuations in membership, unions remain pivotal in today’s economy (OECD 2019). In the US, union approval rates recently reached 70% (Gallup n.d.) – one of the highest levels in 90 years – and the number of workers involved in work stoppages surged by 141% in 2023 (from 224,000 to 539,000) (Ritchie et al. 2023). In other parts of the world, such as Europe, where collective bargaining has a strong tradition, organised labour continues to expand into previously unorganised sectors and influence labour market conditions.
Yet, despite their enduring importance, the empirical evidence on the forces behind unions’ emergence and growth remains limited. In a recent paper (Medici 2024), I examine how mass immigration from Europe to the US during the early 20th century shaped the rise of American labour unions.
How immigration impacts unions is ambiguous. On one hand, increased job competition can motivate workers to unionise to defend wages and employment. On the other hand, a larger labour supply may make it easier for employers to replace uncooperative or striking workers, weakening unions’ bargaining power. Whether immigration fosters or hinders unionisation is ultimately an empirical question.
The early 20th-century US offers a compelling setting to examine this question. The US was already the world’s largest economy (Bolt and Van Zanden 2020), and the labour movement began expanding nationally (Foner 1947). Many unions founded during this period remain influential today. This growth occurred despite significant challenges to organising, as employers could legally dismiss or replace unionising and striking workers without facing penalties (Taft 1964). Immigration played a central role in shaping these dynamics. Between 1850 and 1920, around 30 million European immigrants entered the US, transforming local labour markets and creating both opportunities and challenges for organised labour (Figure 1).
Figure 1 Number of union members and inflow of immigrants to the US, 1880s to 1920
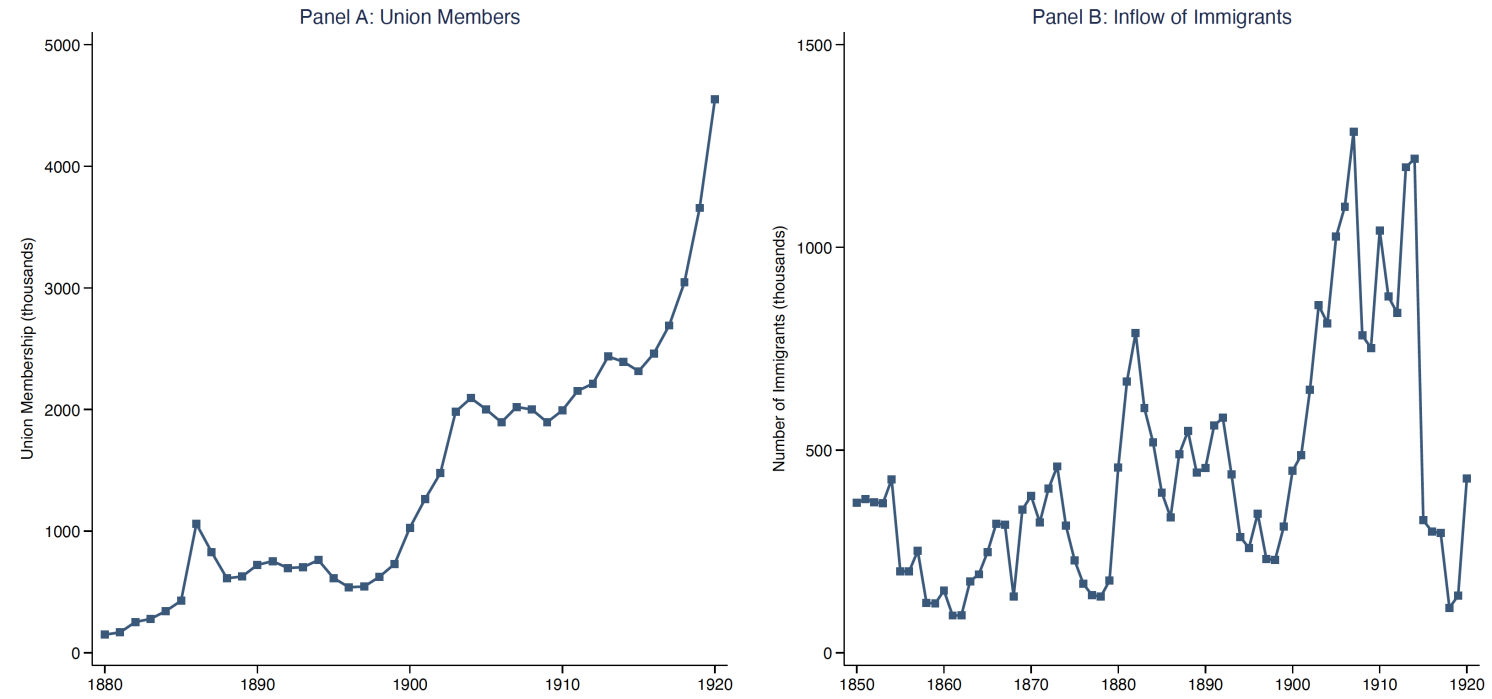
Notes: Panel A shows the total number of union members in the US between 1880 and 1920 (Freeman 1998). Panel B shows the inflow of immigrants to the US between 1850 and 1920 (Immigration Policy Institute).
Studying the relationship between immigration and unions presents two key challenges: measuring local unionisation and establishing causal effects. To measure unionisation, I digitised archival documents on unions affiliated with the American Federation of Labour between 1900 and 1920 – a period when American Federation of Labour unions represented over 80% of union members nationwide. These records, drawn from the convention proceedings of state federations of labour, provide detailed information on the number and location of union branches across the country, and allow me to construct novel estimates of union membership. These data provide the first comprehensive, local-level measurements of historical union presence and density in the US (Figure 2).
To estimate the causal impact of immigration, I employed a shift-share instrumental variable approach (Card 2001). This method leverages chain migration patterns, whereby immigrants tend to settle in areas with established communities from their countries of origin.
Figure 2 County-level union density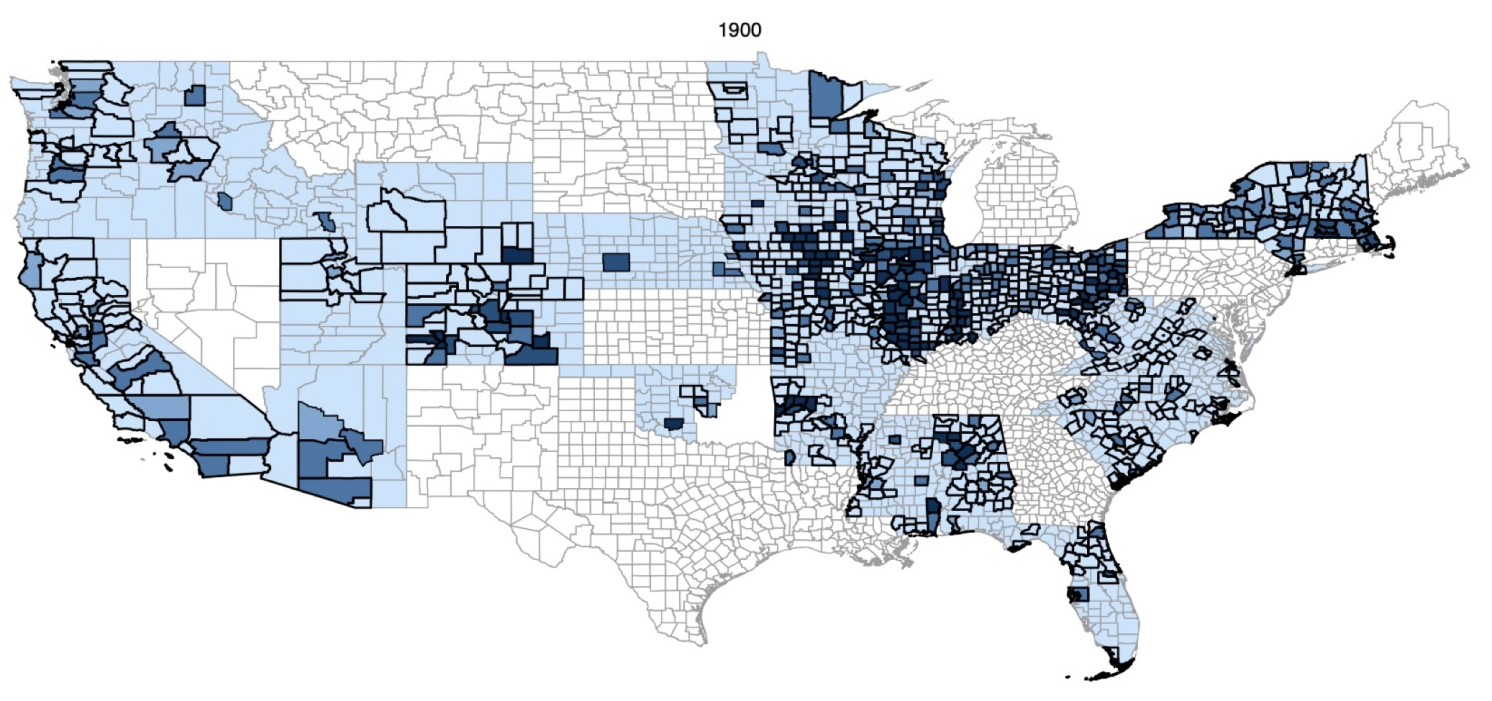
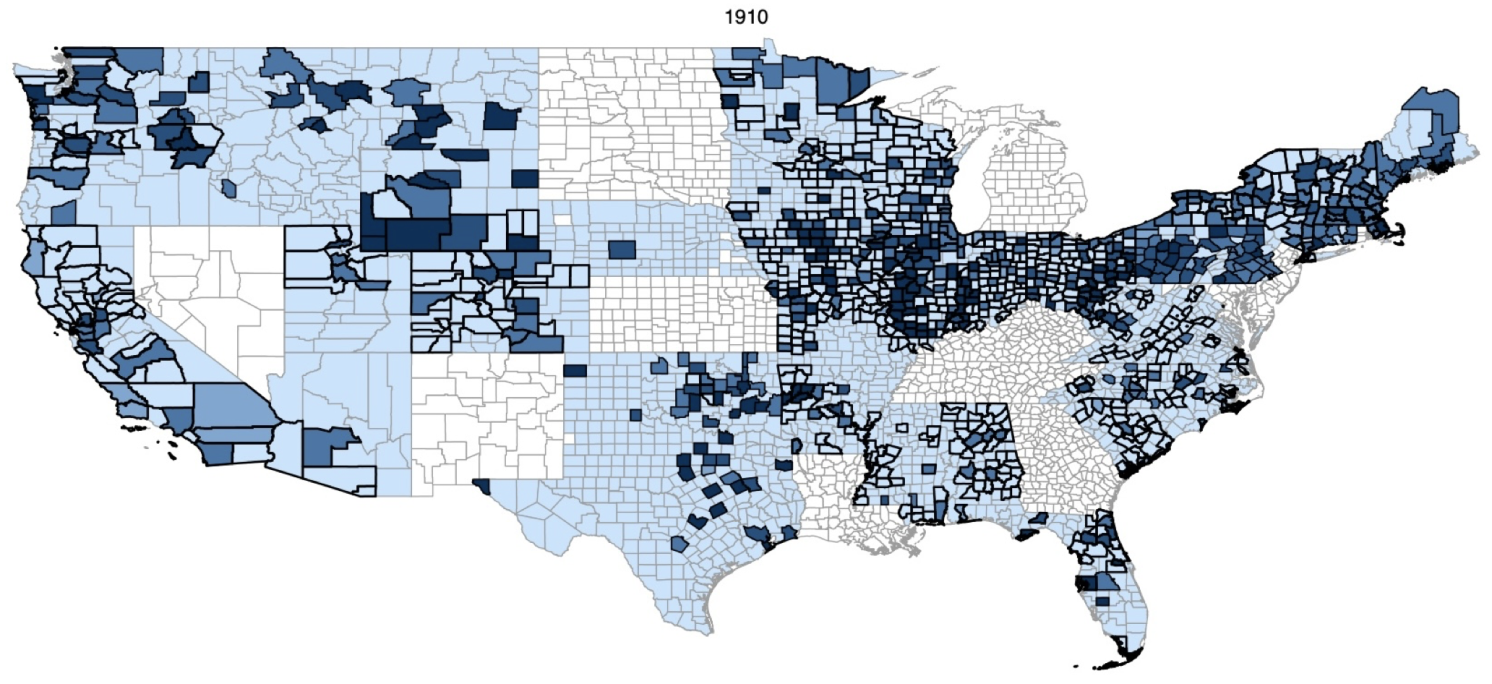
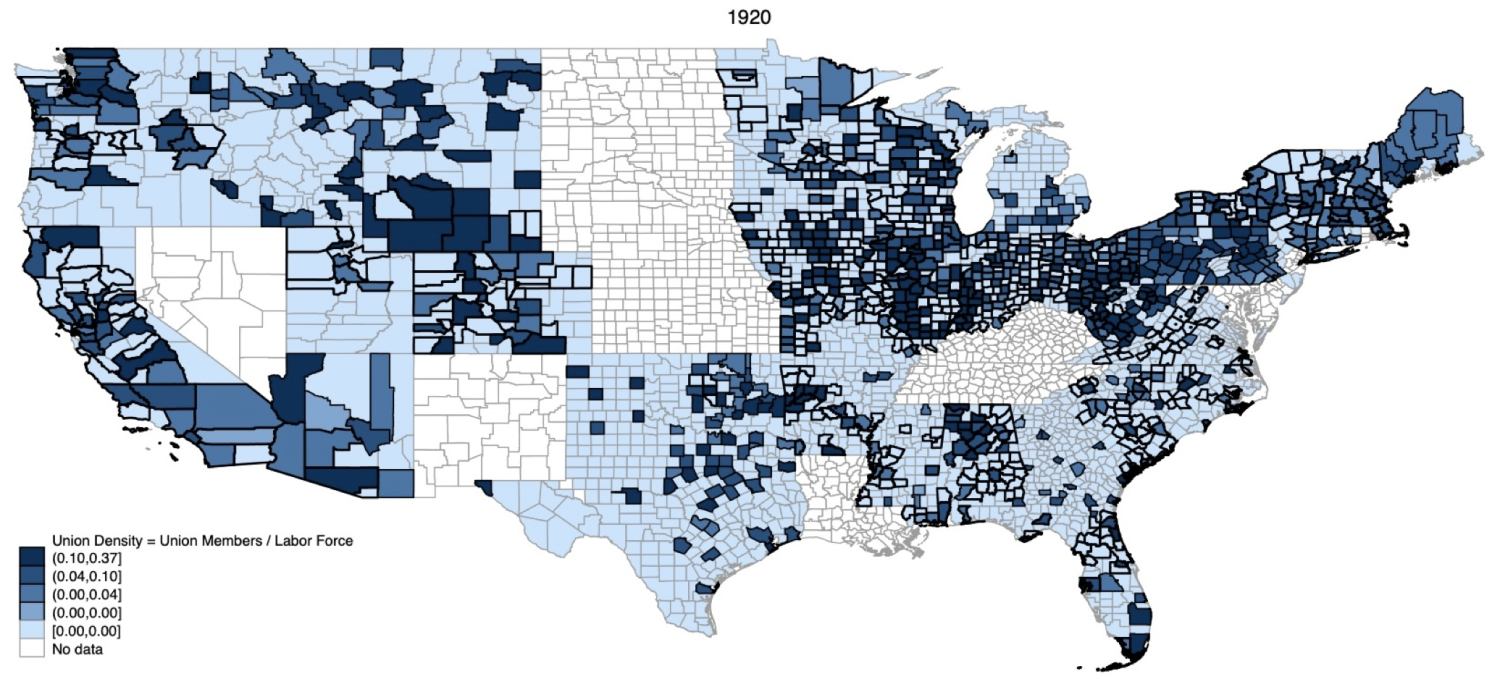
Notes: These maps display county-level union density (i.e. the number of union members as a fraction of the labour force) in 1900, 1910, and 1920. The legend represents the deciles of the distribution in 1920.
Source: Author’s calculations from convention proceedings of the state federations of labour (American Federation of Labour unions).
Main Results
The results show that immigration fostered the emergence of organised labour. Counties that received more immigrants as a share of the population experienced increases in union presence, the number of union branches, the share of unionised workers, and the number of union members per branch.
Immigration spurred unionisation both at the intensive and extensive margins – expanding unions in counties with an existing labour movement and establishing new unions elsewhere. For every 100 immigrants entering the average county, union membership increased by nearly 20 workers. A back-of-the-envelope calculation suggests that without immigration, average union density (i.e. the share of unionised workers) would have been approximately 22% lower between 1900 and 1920.
Mechanisms
Why did immigration promote unionisation? The evidence is consistent with existing workers unionising in response to immigration for economic as well as social motivations.
Immigration affected unions in skilled and unskilled occupations differently: it spurred unionisation among skilled workers but had smaller and statistically insignificant effects for unskilled ones (Figure 3). Skilled workers, such as those in craft occupations, organised to protect their jobs and wages. Their specialised skills acted as barriers to entry, making them not immediately replaceable and enabling them to form or join unions. This allowed them to exclude new workers from their occupations and prevent outsiders from acquiring the skills required for these jobs. In contrast, low-skilled workers, such as labourers, struggled to sustain unions. Their jobs could be easily and immediately filled by newcomers, which reduced their bargaining power and made unionisation efforts in response to immigration largely unsuccessful.
Figure 3 Immigration and unionisation among skilled vs unskilled workers
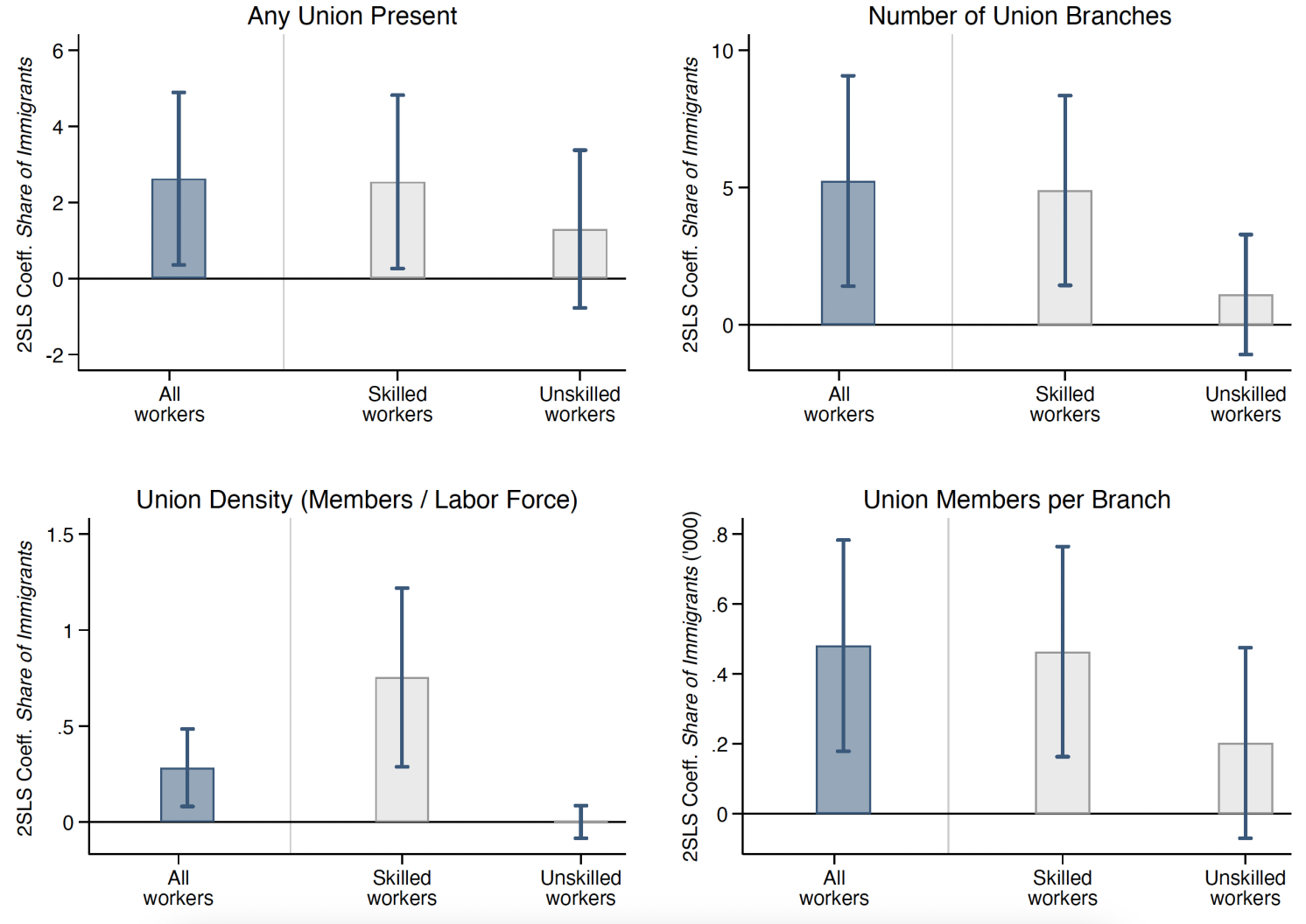
Notes: This figure shows the coefficients and confidence intervals from two-stage least squares regressions examining the effects of immigration on unionisation. The blue bar on the left displays the effect on all workers, while the grey bars on the right show the effects on skilled and unskilled workers separately.
Alongside economic motivations, the results also support the role of social factors in the expansion of labour unions. American Federation of Labour unions often adopted nativist rhetoric, portraying immigrants – particularly those from Southern and Eastern Europe – as culturally distant and less likely to assimilate or unionise effectively. These attitudes were reflected in unionisation patterns. Unionisation grew more prominently in counties that received immigrants from culturally distant regions (Figure 4). It also expanded more in areas that likely displayed stronger anti-immigrant sentiment, such as those with strong historical support for nativist movements like the Know Nothing party or higher levels of residential segregation between immigrants and US-born residents (Figure 5).
Figure 4 Source regions of European immigrants and unionisation
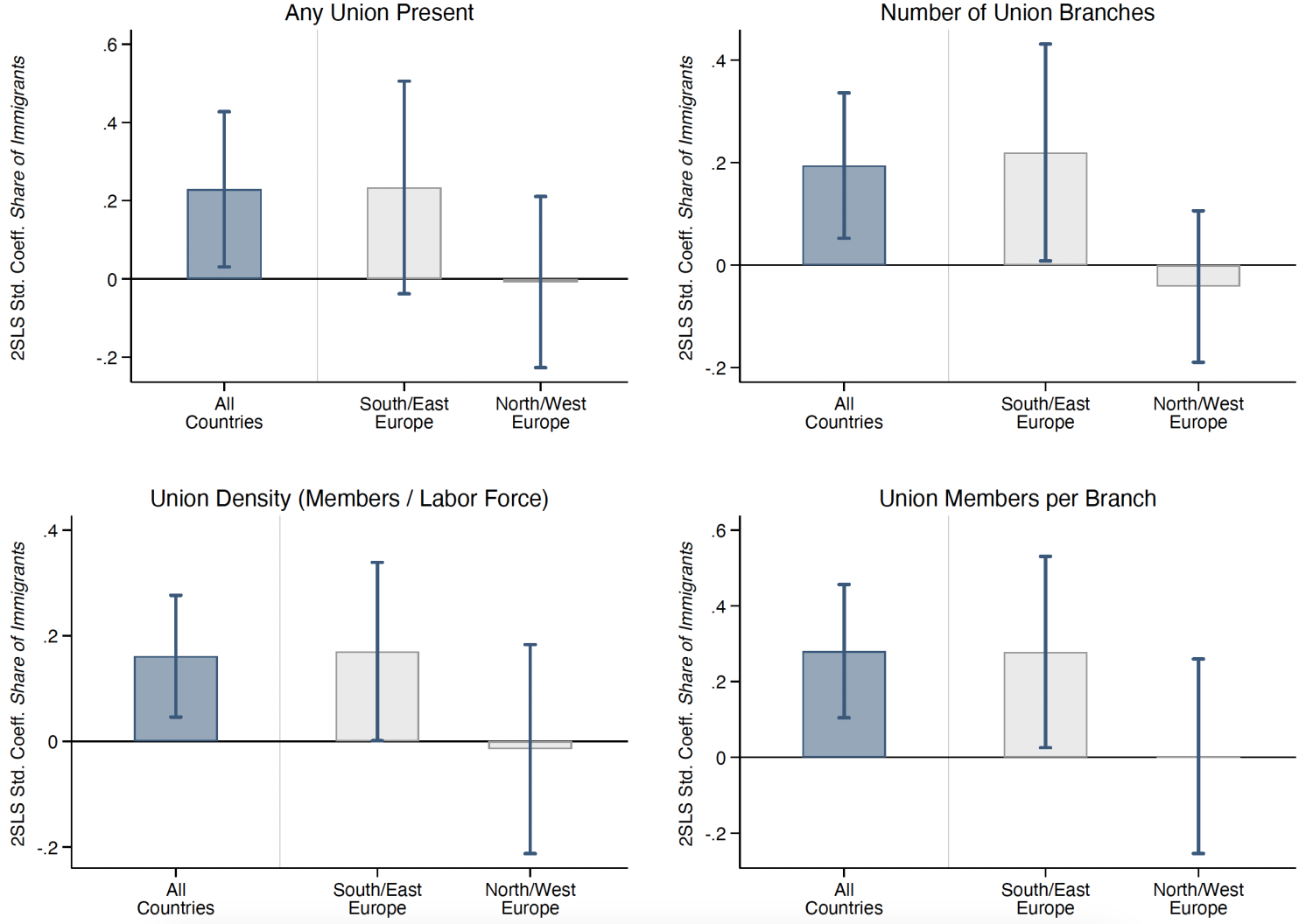
Notes: This figure shows the coefficients and confidence intervals from two-stage least squares regressions examining the effects of immigration on unionisation. The blue bar on the left displays the effect of immigrants from any European country, while the grey bars on the right show the effects of immigration from Southern and Eastern Europe or Northern and Western Europe separately.
Figure 5 Local anti-immigrant sentiment and unionisation
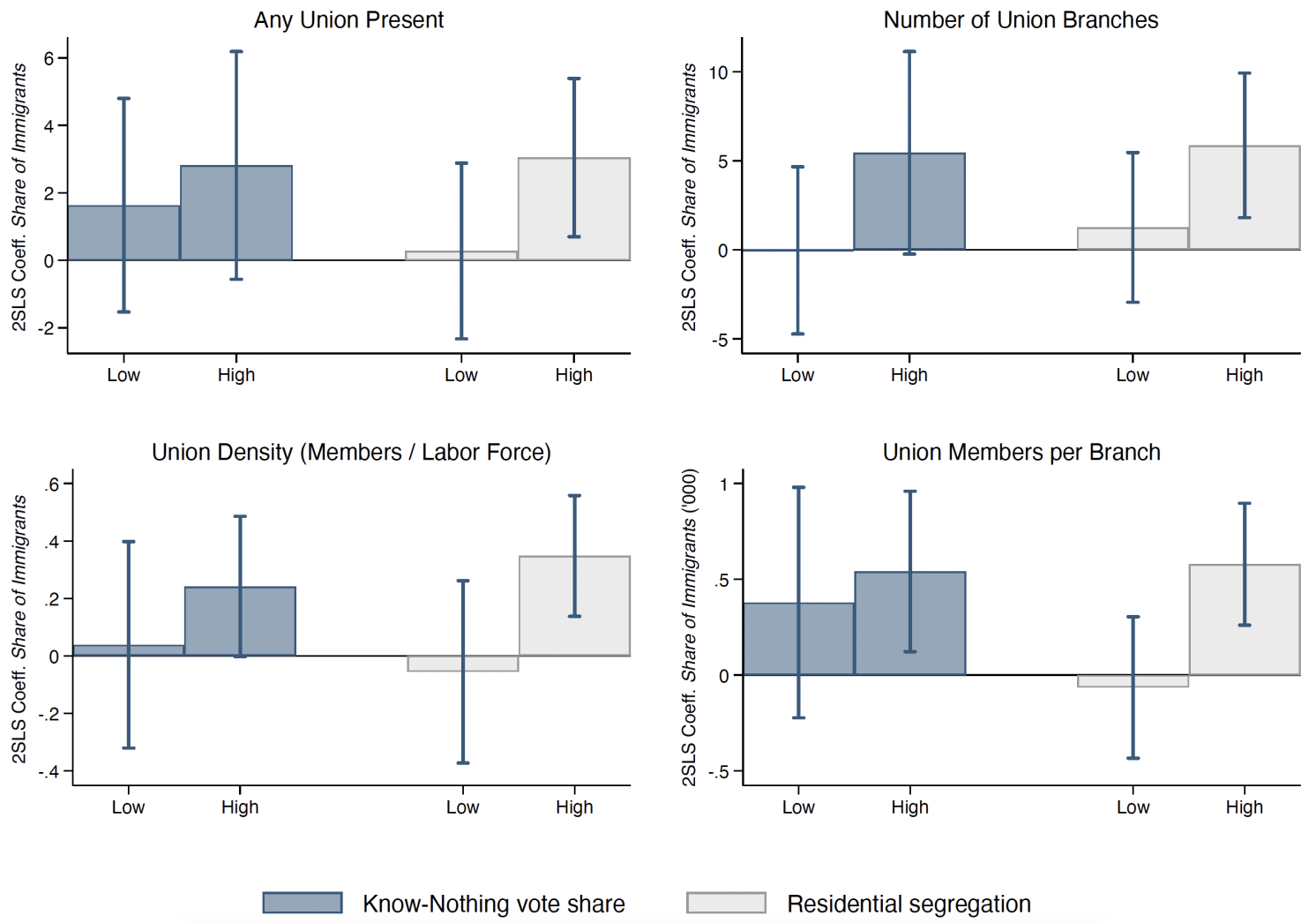
Notes: This figure shows the coefficients and confidence intervals from two-stage least squares regressions examining the effects of immigration on unionisation. The blue bars on the left display the effects for counties with low and high historical vote shares of the Know Nothing party. The grey bars on the right show the effects for counties with low and high baseline levels of residential segregation between US-born individuals and European immigrants.
It is important to note that these results are also consistent with economic explanations. Immigrants from Southern and Eastern Europe likely had lower wage expectations than those from Northern and Western Europe, making them more likely to be perceived as a threat to existing workers’ conditions. Moreover, fears of economic competition from immigrants may have amplified negative stereotypes and reinforced pre-existing resentment. Overall, the results support the role of both economic and social factors in driving the observed growth of organised labour.
Alternative explanations, such as immigrants disproportionately joining unions or bringing radical ideologies from their home countries, are not supported by the data. The results are also not driven by other major events during this period, such as the political and economic transformations caused by World War I and the First Red Scare, or by differential economic growth experienced by counties receiving larger shares of immigrants.
Long-Term Implications
The effects of early 20th-century immigration on unionisation extend well beyond the historical period studied. Places that received more immigrants between 1890 and 1920 continue to exhibit higher union density today, suggesting that early unionisation created durable institutional advantages for organised labour.
Immigration also reshaped occupational choices. US-born workers increasingly took unionised jobs, likely using organised labour as protection against immigrant competition.
Conclusion
This research identifies immigration as a key driver of unionisation during the formative years of the American labour movement. By examining how immigration shaped organised labour, the study highlights the economic and social forces that influence labour market institutions.
These findings also broaden our understanding of the consequences of immigration, showing that responses to large immigrant inflows are not limited to increased support for conservative parties or anti-immigration policies. Instead, immigration can foster the growth of organisations, such as unions, with broad economic and political impacts.
While the historical context is unique, the results point to broader mechanisms that remain relevant today. Renewed interest in unions may reflect workers’ responses to modern labour market pressures – such as immigration, globalisation, and technological change. These dynamics are not confined to the US. They also resonate with advanced economies facing similar challenges and with industrialising nations undergoing economic transformations comparable to early 20th-century America.
Further research is needed to examine how organised labour responds to economic shocks in different contexts. The dataset assembled for this study provides new opportunities to investigate many additional questions, such as the long-term impact of early unionisation on immigrant integration and its broader impact on the US economy and political landscape.
See original post for references